What is Arc Strike?
Arc strike, also known as arc burn, refers to a welding flaw that occurs when the electric arc comes into unintended contact with the base metal or a previously welded area where it is not supposed to be applied.
This can happen if the welding arc is initiated in the wrong location or if the welder accidentally touches the electrode or filler material to the incorrect area before establishing the proper welding position.
Arc strike involves the initiation of an arc on the surface of the base metal, away from the intended weld zone. This unintentional or intentional arc creates a localized area where the base metal is melted and rapidly cooled due to the surrounding metal acting as a heat sink.
As a result, the structure of the base metal undergoes changes, becoming hard and brittle. This alteration increases the risk of cracking, which can ultimately lead to the failure of the weldment. Therefore, arc strike is considered a critical discontinuity that needs to be carefully managed in welding processes.
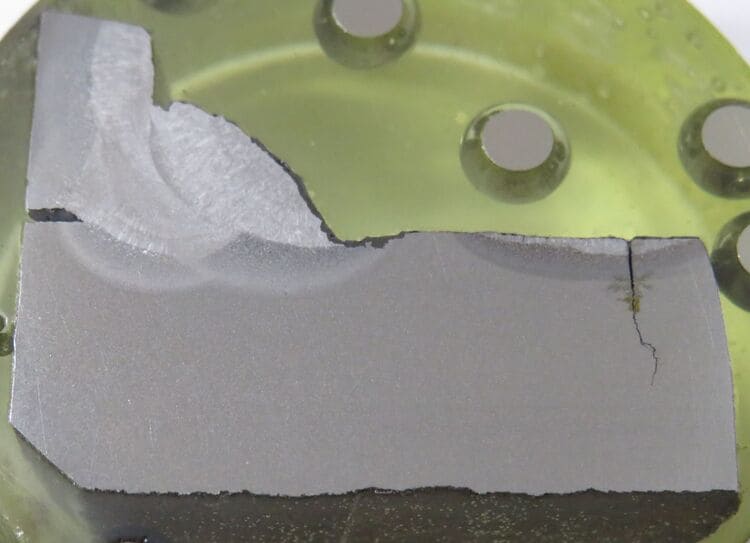

In above example, The area affected by the melted zone of the arc strike exhibited a hardness of approximately 350 HV, while the heat-affected zone (HAZ) adjacent to it had a hardness of 400 HV.
The weld metal and its immediate HAZ displayed a hardness ranging from 200 to 250 HV. Comparatively, the base metal had a hardness of 150 HV. The material in question was SA-299, which had a carbon content of 0.16% and a manganese content of 1.4%.
Adverse effects of Arc Strike
Adverse effects of arc strikes can have several negative consequences on welded joints. These include:
- Contamination: When an arc strike occurs, it can melt and fuse the base metal or previous weld, leading to contamination. This contamination can adversely affect the mechanical properties and overall integrity of the welded joint.
- Cracking: The rapid heating and cooling caused by an arc strike create localized thermal stress, which can result in cracks within the welded area.
- Weakened Weld: Arc strikes introduce defects and irregularities in the weld bead, weakening the overall strength of the weld.
- Inconsistent Weld Appearance: Arc strikes can cause irregularities in the appearance of the weld, making it look uneven and visually unappealing.
- Reduced Weld Quality: Depending on the severity of the arc strike and the specific welding application, the overall quality and performance of the weld can be compromised.
Why Arc Stike in Bad?
Arc strikes are considered undesirable in welding for several reasons. Firstly, they can cause contamination in the weld.
When an arc strike occurs, it melts and fuses the base metal or previously deposited weld in unintended areas. This can introduce impurities and foreign materials into the weld, compromising its quality and strength.
Secondly, arc strikes can weaken the weld. They introduce defects and irregularities in the weld bead, creating stress concentration points. These weak spots can lead to cracking or even complete failure of the weld under applied loads or stress.
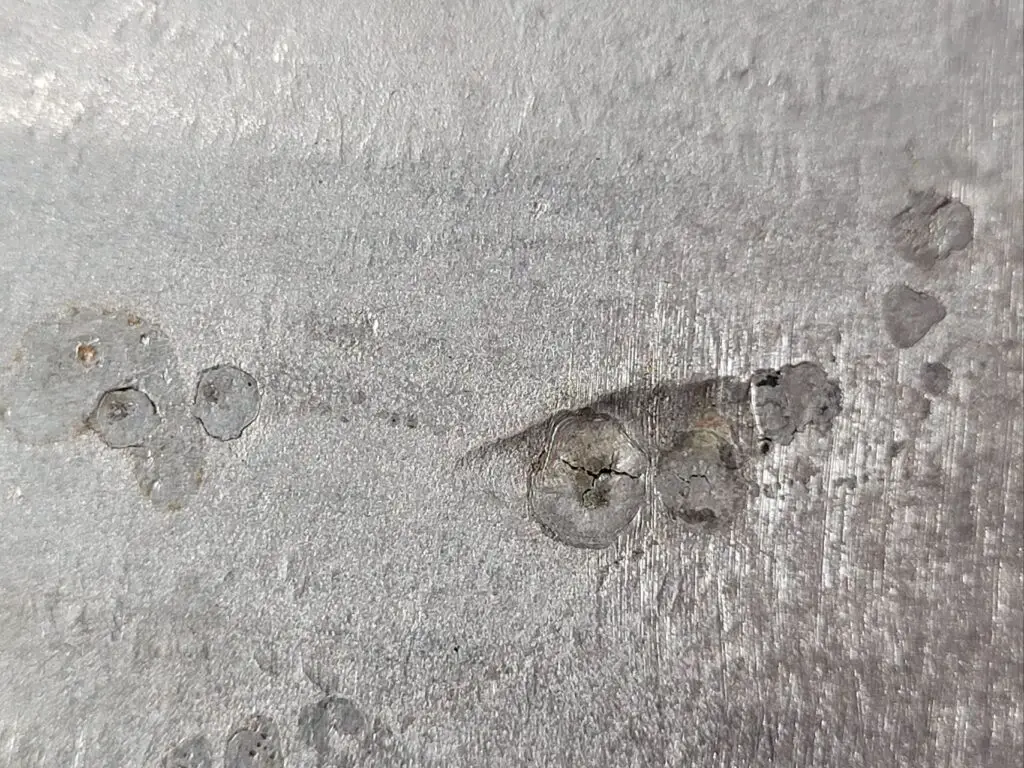

Thirdly, arc strikes can have a negative impact on the appearance of the weld. They can create uneven weld beads, surface irregularities, or discoloration, making the weld look aesthetically unappealing and unprofessional.
How to Prevent Arc Strike?
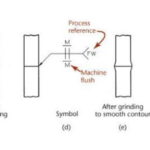
To address arc strikes, it is necessary to remove them by grinding. By grinding to a depth of 1/8 inch below the original surface, all traces of arc strikes and their hardened heat-affected zones can be eliminated.
In areas where the arc strikes have been removed, it is important to conduct magnetic-particle inspection and hardness testing to ensure the integrity of the weld.
Preventing arc strikes requires welders to employ proper techniques and positioning when initiating and maintaining the welding arc.
This involves starting the arc in the intended location and ensuring that the electrode or filler material does not accidentally touch the base metal outside the desired weld zone. Welders should also wear appropriate protective gear, such as gloves and helmets, to prevent accidental contact between the electrode and their skin.
In industries where weld quality and integrity are crucial, comprehensive training, adherence to safety protocols, and meticulous attention to detail are essential to minimize the occurrence of arc strikes and other welding defects.
Can you Weld over Arc strike?
Welding over an existing arc strike is generally not recommended. Arc strikes can introduce defects, contamination, and changes in the base metal’s properties, which can negatively impact the weld quality and integrity. Welding over an arc strike without addressing it properly can lead to further complications and potential welding defects.
Before attempting to weld over an arc strike, it is advisable to remove the affected area. This typically involves grinding or machining to remove the hardened or contaminated material caused by the arc strike. By removing the arc strike and any associated heat-affected zones, you can create a clean surface for the subsequent weld.
After removing the arc strike, it is essential to inspect the area to ensure all traces of the strike have been eliminated. Visual inspection, magnetic particle inspection, or other non-destructive testing methods may be necessary to verify the cleanliness and integrity of the base metal before proceeding with the weld.