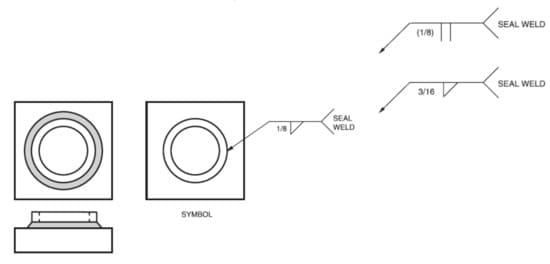
What is a Seal Weld?
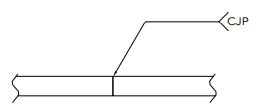
A seal weld refers to a specific type of weld that is applied to create a seal or closure between two surfaces. It is commonly used to prevent the leakage or ingress of fluids, gases, or other substances in various industrial applications.
The primary purpose of a seal weld is to provide a tight, secure, and impermeable joint.
By MaterialWelding
Seal welds are typically applied along the entire length or perimeter of a joint, ensuring complete sealing between the surfaces.
According to AWS A3.0, Standard Welding Terms and Definitions, “a seal weld is defined as a weld primarily intended to achieve a specific level of tightness to prevent leakage”. The main purpose of a seal weld is often to contain either a gas or liquid substance.
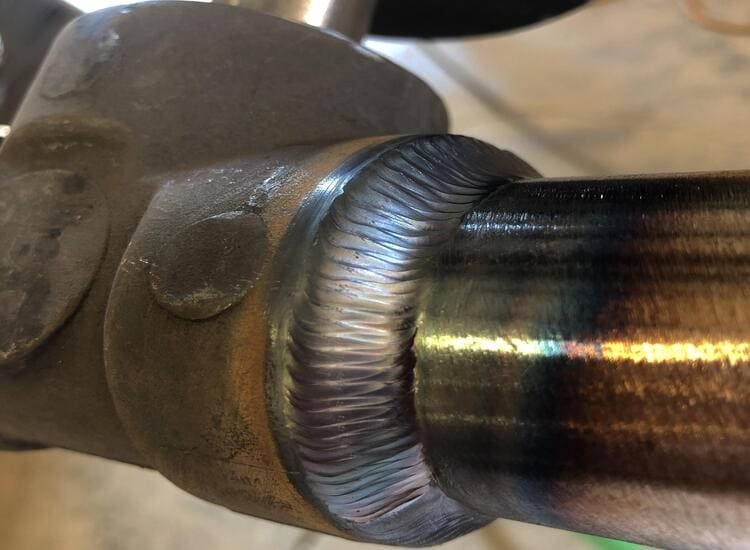

What are the applications of Seal Weld?
The main applications of seal welding are:
- In mechanical and structural fields, seal welds are commonly used not only to prevent leakage from a container but also to prevent the entry of fluids into spaces where detrimental effects, such as corrosion, are expected. These welds are frequently employed to keep out moisture, oxygen-laden air, and water that can lead to corrosion.
- In certain cases, seal welds are specified on parts that will undergo galvanization to prevent the entry of pickling acids or liquid zinc into specific areas.
- For architecturally exposed steel that will be painted, seal welds may be specified to prevent unsightly rust bleeding.
- Seal welds are also utilized in applications where a sealed joint is easier to clean compared to an exposed joint, such as in food processing facilities.
Difference between seal weld and strength weld
When we use comparison term for Seal Weld vs Strength Weld, it usually refers to the weld joing between tube to tubesheet of heat exchanger. Seal Welding Symbol tail section usually mention it either a seal weld or strength weld.
A seal weld is applied solely for the purpose of achieving enhanced leak tightness. In many cases, when performing seal welds, the tube is welded to the tubesheet without the use of filler metal. However, in certain cases, filler metal may be employed, particularly for specific metallurgies such as 410 stainless steel.
Typically, the tube extends beyond the surface of the tubesheet by 1/8″. During welding, the tube melts and fuses with the tubesheet to create a solid joint. It is important to note that the tube hole in the tubesheet does not require beveling for a seal weld.
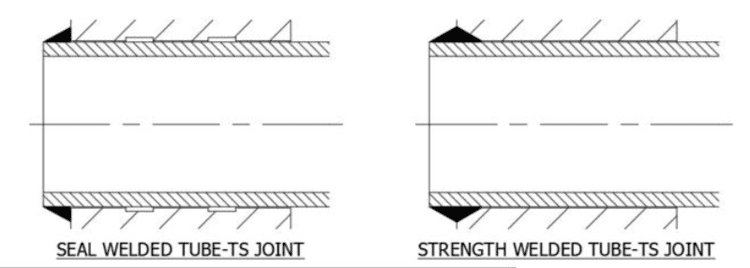
On the other hand, a strength weld serves the dual purpose of bearing longitudinal tube loads and offering additional leak tightness.
The procedure for a strength weld is similar to that of a seal weld, except that the tube hole in the tubesheet is beveled (e.g., with a 45-degree bevel or a j-groove) to allow for the deposition of filler metal. Typically, a strength weld involves a two-pass welding process.
| Aspect | Seal Weld | Strength Weld |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Primarily to provide tightness against leakage | Primarily to achieve structural strength |
| Leakage Control | Designed to prevent fluid ingress or egress | Not specifically focused on leakage control |
| Application | Used to prevent the entry of fluids, gases, or substances | Used to create structurally sound joints |
| Common Usage | Preventing corrosion, moisture, or undesired substances from entering a space | Joining structural components, load-bearing applications |
| Joint Integrity | Emphasizes achieving a specific degree of tightness | Emphasizes achieving mechanical strength |
| Appearance | May not have strict appearance requirements | Appearance may be secondary to strength requirements |
| Cleaning | In some applications, sealed joints are easier to clean | Cleaning considerations may vary depending on the joint |
| Welding Process | Various welding processes can be used, depending on the application | Various welding processes can be used, depending on the application |
| Standards/Specs | Specific standards and specifications may apply for seal welds | Specific standards and specifications may apply for strength welds |