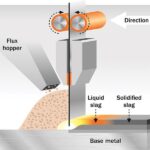
Cladding is a versatile surfacing technique used to deposit or apply a protective layer of material onto a metal surface. It is commonly employed to enhance corrosion resistance, heat resistance, or wear resistance.
Cladding can be achieved through various methods, including welding, thermal spraying, or other specialized techniques.
In this blog post, we will explore the concept of cladding in welding, its advantages and disadvantages, and its applications in different industries.
What is Cladding in Welding?
Cladding in welding involves the deposition of a filler metal with desirable properties onto the base metal. This filler metal is carefully chosen to enhance the surface characteristics of the base metal.
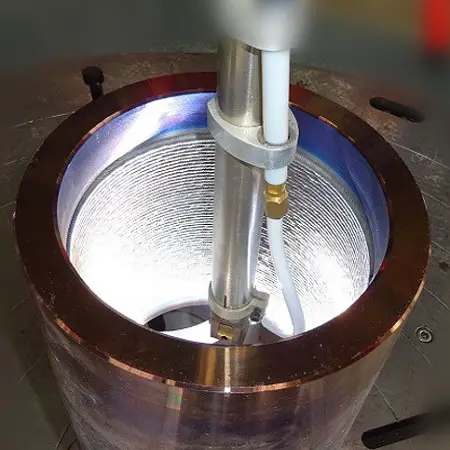

The filler metal and base metal are then fused together, forming a strong metallurgical bond. This process can be utilized to repair damaged surfaces or safeguard new surfaces from wear and tear.
Thermal Spraying as a Cladding Method
Another method of cladding is thermal spraying. In this technique, molten particles are sprayed onto the surface of the base metal. These particles fuse together, creating a protective coating.
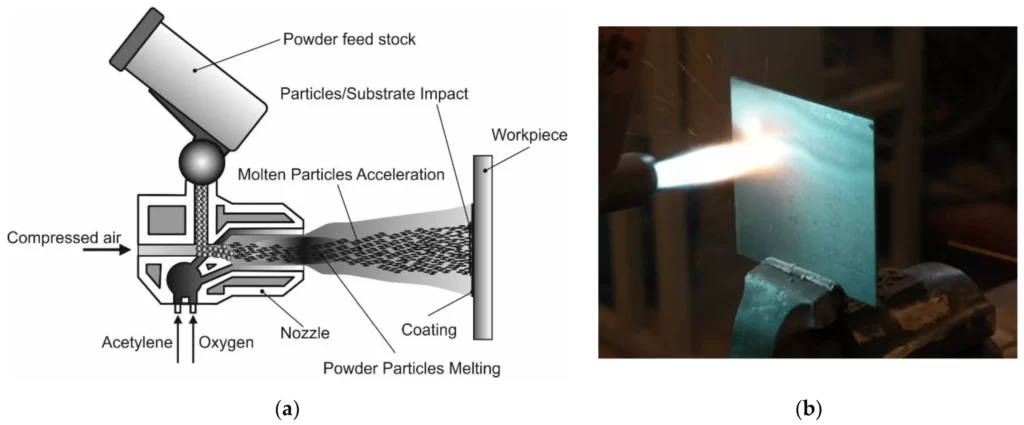
Thermal spraying allows for the application of coatings made from various materials, including metals, ceramics, and plastics.
Advantages of Cladding
Cladding offers several advantages in enhancing metal surfaces:
- Improved Surface Properties: Cladding significantly enhances the surface properties of a metal, such as corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and heat resistance.
- Surface Repair: Cladding can effectively repair damaged surfaces, restoring their functionality and extending their lifespan.
Disadvantages of Cladding
While cladding provides numerous benefits, it also has some drawbacks:
- Cost: The cladding process can be relatively expensive due to the specialized materials and equipment required.
- Time-Consuming: Cladding can be a time-consuming process, especially when dealing with complex surfaces or intricate geometries.
Understanding Clad Welding
Clad welding is a specific type of welding that involves depositing a filler metal onto the base metal. The filler metal and base metal are then fused together, forming a strong metallurgical bond.
This technique is employed to improve the surface properties of the metal, resulting in enhanced corrosion resistance, wear resistance, or other desired characteristics.
Differentiating Cladding and Weld Overlay
Cladding and weld overlay are similar techniques used to enhance metal surfaces, but they have distinct differences. Cladding is versatile and can be used for surface repair or protection, while weld overlay is primarily focused on improving surface properties without the repair aspect.
Heat Exchanger Cladding
Heat exchanger cladding is a specialized process where a thin layer of metal is deposited onto the surface of a heat exchanger. This thin metal layer enhances the heat transfer properties of the heat exchanger, improving its overall efficiency.
Hard Facing in Welding
Hard facing is a process that involves depositing a hard, wear-resistant material onto the surface of another metal. This technique is commonly used to enhance the wear resistance of a metal, making it suitable for applications subjected to high levels of abrasion.
Buttering Welding
Buttering welding is a technique that entails depositing a thin layer of material onto the surface of another metal. This process is often employed to enhance the corrosion resistance or wear resistance of a metal, providing added protection in harsh environments.