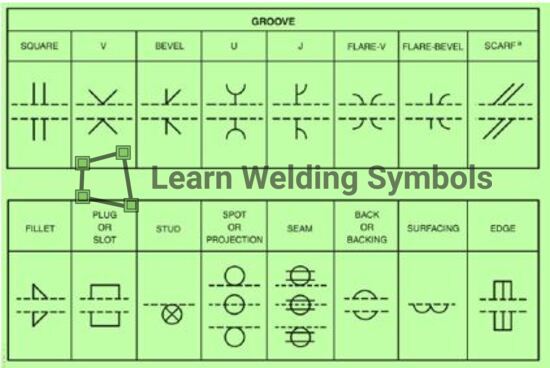
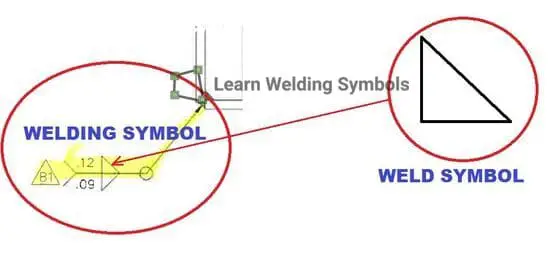
Lap Weld Symbol
The lap weld symbol is a specific welding symbol used to represent a lap joint in welding. It signifies that two overlapping workpieces are to be joined together by welding along the overlapping edges.
In addition to the basic lap weld symbol, there may be additional specifications included to provide further details about the weld, such as the weld size, weld length, and any additional required information. These specifications are typically placed next to or below the lap weld symbol.
What is a Lap Weld?
A lap weld refers to a type of welding joint where two overlapping workpieces are joined together by welding along the overlapping edges. In this joint configuration, one workpiece is placed on top of the other, creating an overlap. The welding process is then applied to fuse the overlapping regions, forming a strong and continuous weld.
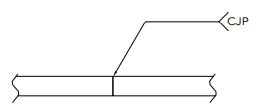
Lap Weld Symbol
The lap weld symbol, similar to the fillet weld symbol, is commonly used to represent a lap joint in welding. However, there are instances where the lap weld requires a bevel groove preparation instead of a simple fillet joint.
In such cases, a bevel groove weld symbol is used to indicate the specific requirements for the lap weld.
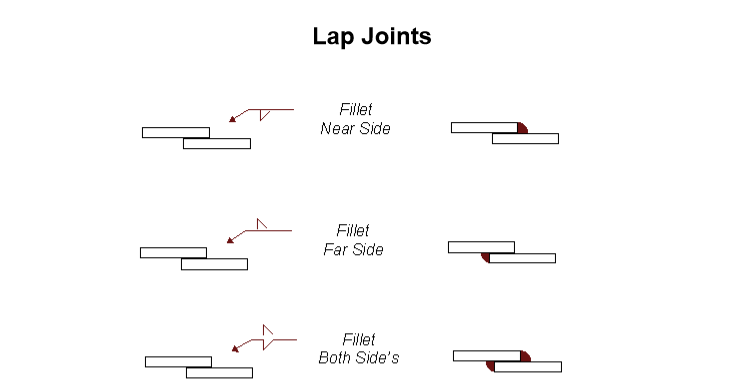
A Lap weld joint with complete welding symbol for having a Fillet weld consists of:
- A arrow line,
- reference line,
- fillet weld symbol placed on the reference line,
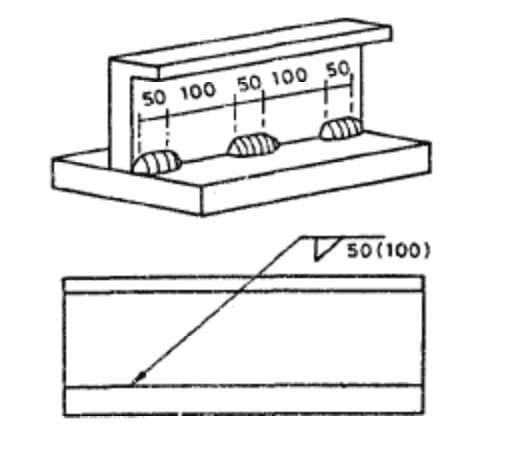
- weld size and weld length,
- tail to provide additional information.
The bevel groove preparation for a lap weld involves creating a sloped or angled edge on one or both of the workpieces to achieve a more robust and complete weld penetration.

The bevel angle and dimensions are typically specified in the bevel groove weld symbol to ensure proper joint preparation and welding procedure.
Application of Lap Weld
Lap welds find application in various industries and scenarios where two overlapping workpieces need to be securely joined together. Some common applications of lap welds include:
- Sheet Metal Fabrication: Lap welds are frequently used in sheet metal fabrication to join thin metal sheets together. They provide a strong and visually appealing joint, making them suitable for applications such as automotive body panels, enclosures, cabinets, and ductwork.
- Structural Welding: Lap welds are employed in structural welding to join structural members, such as beams, plates, and angles. They are often used in construction, bridges, and framework fabrication, where strength and load-bearing capacity are essential.
- Piping Systems: Lap welds are utilized in the construction and maintenance of piping systems. They enable the connection of pipes, fittings, and flanges, ensuring fluid-tight joints. Lap welds are commonly used in industries like oil and gas, chemical processing, and plumbing.
- Automotive Manufacturing: Lap welds are frequently employed in the manufacturing of vehicles, including cars, trucks, and motorcycles. They are used to join various components, such as body panels, brackets, and chassis elements, providing structural integrity and rigidity.
- Shipbuilding: Lap welds play a vital role in shipbuilding, where they are used to connect metal plates and sections to construct the hull, decks, and bulkheads of ships and boats. The lap welds used in this industry undergo rigorous testing and inspection to ensure the integrity and seaworthiness of the vessels.
- Furniture Manufacturing: Lap welds are utilized in the production of metal furniture, including chairs, tables, and cabinets. They facilitate the assembly of metal frames, joints, and connections, providing stability and durability to the furniture pieces.
- General Fabrication: Lap welds are commonly employed in various general fabrication applications, including welding brackets, brackets, panels, and other components in industries such as aerospace, appliances, and machinery manufacturing.
Frequently asked questions (FAQS)
What is the difference between a lap joint and a butt joint?
A lap joint and a butt joint are two different types of welding joints. In a lap joint, two workpieces overlap each other, and the welding is done along the edge where they overlap.
In contrast, a butt joint is formed when two workpieces are aligned edge-to-edge, and the welding is done along the seam where the edges meet. Butt joints require more precise preparation and alignment of the edges compared to lap joints.
Can lap welds be used for load-bearing applications?
Yes, lap welds can be used for load-bearing applications, but the suitability depends on various factors such as the material being welded, the joint design, and the specific loading conditions.
Lap welds can provide adequate strength and structural integrity when properly executed and designed to handle the anticipated loads. It is important to consult relevant codes, standards, and engineering guidelines to determine the appropriate joint design and welding parameters for load-bearing lap welds.
What are the advantages of lap welding?
Some advantages of lap welding include:
- Simplicity: Lap welding is relatively simple and straightforward compared to some other welding techniques.
- Cost-effective: Lap welding often requires less material and preparation compared to other joint configurations, making it cost-effective.
- Versatility: Lap welds can join different thicknesses and types of materials, enabling versatility in various applications.
- Aesthetics: Lap welds can provide a visually appealing joint, especially when executed with precision.
- Flexibility: Lap joints allow for some tolerance in fit-up and alignment, making them more forgiving in certain situations.
It is important to note that while lap welding offers these advantages, the specific application, design, and welding parameters need to be carefully considered to ensure the integrity and strength of the weld for the intended purpose.
Can lap welds be used on non-metallic materials?
No, lap welds are specific to metal welding and cannot be directly applied to non-metallic materials. Non-metallic materials, such as plastics or composites, typically require different joining techniques specific to their properties, such as adhesive bonding, thermal bonding, or mechanical fastening methods.