Reinforcing bar standees (〰️➰〰️), commonly referred to as rebar standees, play a crucial role in supporting top mats of reinforcing bars in thick concrete structures like footings and slabs. This comprehensive guide explores the functionality, various types, and important design considerations for rebar standees.
Understanding the Functionality of Rebar Standees
〰️〰️〰️〰️ Rebar, also known as reinforcing bar〰️〰️〰️〰️, is incorporated into concrete to enhance its tensile strength, thereby minimizing the risk of cracking and breaking. Rebar standees ➰➰, typically made from reinforcing bars, serve as a prevalent form of bar support, especially for heavy reinforcement mats or elevated supports.
Exploring Different Types of Rebar Standees
- ✔️Bend Type 25: Widely used for swimming pool frames, road and highway paving, patio and driveway construction, and even in agricultural applications.
- ✔️Bend Type 26: Known for its stability under vertical load, although it lacks adjustable height functionality.
- ✔️Shape 27: A modified version of Bend Type 26, often utilized near slab edges, requiring tie-downs to prevent tipping.
- ✔️Shape S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6 & S11: Offers a single-plane shape that can be bent using standard tie benders, allowing easy height adjustment. Tall standees may require lateral bracing.
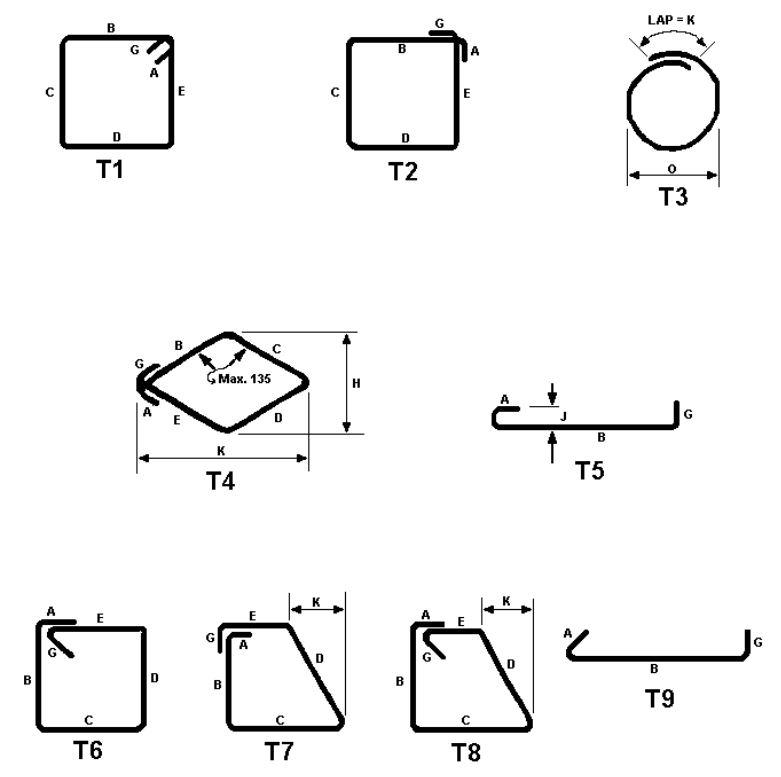
- ✔️Bend Type T1, T2, t3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9 Rebar Standee
Bend Type 24 Rebar Standee
✨✨ The Bend Type 24 rebar standee is a reinforcing bar assembly characterized by its hook-shaped configuration. This shape allows the standee to securely hold and support the top mats of reinforcement in concrete structures.
✨ The hook design provides a reliable and robust connection, ensuring the stability and load-bearing capacity of the standee. Bend Type 24 rebar standees are commonly used in various construction applications where a hook-type shape is beneficial for reinforcing concrete elements.
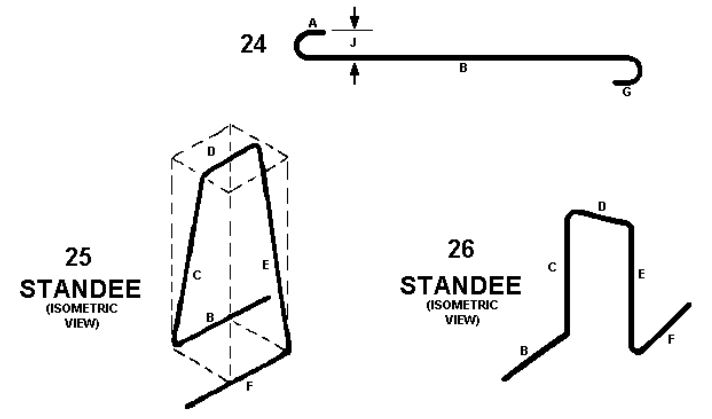
Bend Type 25 Rebar Standee
✨✨ Bend Type 25 rebar standees are primarily utilized in various construction projects, including swimming pool frames, road and highway paving, patio and driveway construction, and even in agricultural applications such as trellising systems.

These standees are constructed from carbon-steel composites with an expansion coefficient that aligns with the properties of industrial-grade concrete.
Bend Type 26 Rebar Standee
✨✨ Bend Type 26 rebar standees are reinforcing bar assemblies designed to provide support for heavy mats of reinforcement or supporting mounts in concrete structures. They feature a fixed height and a unique “U” shape with two vertical legs for stability.
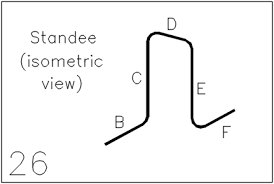
✨✨These standees are commonly used in construction projects where vertical load support is crucial, such as in footings, slabs, high-rise buildings, bridges, and structural foundations.
When incorporating Bend Type 26 standees, it is important to consider load requirements, structural stability, and adherence to engineering specifications to ensure proper alignment and reinforcement support.
Bend Type 27 Rebar Standee
✨ Shape 27 is a modified version of Bend Type 26 rebar standees that are employed by certain fabricators, particularly near slab edges. Unlike Bend Type 26, Shape 27 has both feet pointing in the same direction, which can make it prone to tipping.
✨ To address this, tie-downs may be necessary to ensure stability. An effective technique to mitigate the tipping tendency is by alternating the direction of the legs from one standee to the next during installation.
✨ It’s important to note that Type 25, Type 26, and Type 27 rebar standees are classified as multiple-plane bend bars. Unlike flat bars, these standees have bends and do not lie flat. Due to their non-standard shape, they are referred to as “special fabrication” within the industry. This distinction highlights the need for careful consideration and specialized fabrication techniques when working with these standees.
Bend Type S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6 & S11
Rebar bend shapes S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, and S11 are specific configurations used for reinforcing bars in construction applications. Each shape has its own unique characteristics and purposes.
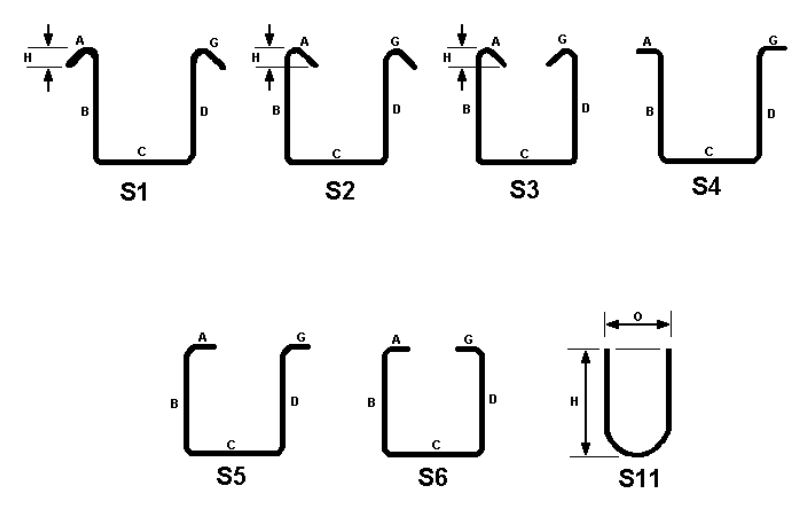
Here’s a brief overview of these rebar bend shapes:
- 💫 Shape S1: This bend shape features a single-plane bend at a specific angle, typically used for creating simple bends in reinforcing bars.
- 💫 Shape S2: Similar to S1, Shape S2 also has a single-plane bend but at a different angle, providing flexibility in design and reinforcement placement.
- 💫 Shape S3: S3 consists of multiple bends in different planes, allowing for complex configurations and reinforcement arrangements in concrete structures.
- 💫 Shape S4: This bend shape involves multiple bends in a single plane, offering versatility in reinforcement placement and adapting to specific project requirements.
- 💫 Shape S5: S5 is designed with multiple bends in different planes, enabling more intricate reinforcement layouts and accommodating complex structural designs.
- 💫 Shape S6: S6, like S1 and S2, has a single-plane bend, but it provides the added benefit of easy height adjustment. It is commonly used when adjustable standees or elevation changes are required.
- 💫 Shape S11: S11 features multiple bends in different planes, offering enhanced flexibility for reinforcement placement in complex structural elements.
Bend Type T1, T2, t3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9 Rebar Standee
In construction, rebar (reinforcing bar) is often bent to specific shapes to enhance its structural properties and provide reinforcement within concrete structures.
✔️✔️The bend designations, such as T1, T2, t3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, and T9, are typically used to describe different bend shapes or configurations as shown in the below picture. ✔️✔️
Taking Design Considerations into Account
When designing rebar standees, several factors should be carefully considered:
- Choosing appropriate bar supports with expansive bearing surfaces to prevent settlement or piercing into the base material.
- Ensuring a large margin of safety and compliance with jurisdiction regulations, particularly for standees exceeding 4 ft (1.2 m) in height.
- Determining the appropriate size of the reinforcing bar, usually one size smaller than the bars to be supported, considering factors like spacing, top layers, and standee height.
- Conducting column stability analysis on standee legs and collaborating with bar placers during installation to ensure reinforcement and support system alignment.
- Providing sufficient breadth in the standee design to maintain proper flat length and prevent the supporting bar from rolling off the top.
Addressing Support Requirements
While standees can be installed to any depth if they adequately brace against lateral and twisting movement, additional support may be necessary for heights exceeding approximately 6 ft (1.8 m). Scaffolding, welded reinforcing bar frames, or structural steel angles can be employed as viable solutions.
Bar Support Recommendations for Foundation Mats and Slabs
Spacing of bar supports for slabs on ground or on a mud-mat should be determined based on the design guidelines. These recommendations should be adjusted to account for the specific weight and rigidity requirements of the specified reinforcing steel.
In general, the bar supports indicated are estimated and provided for slabs up to 4 feet (1200 mm) thick, unless stated otherwise in the project drawings or specifications.
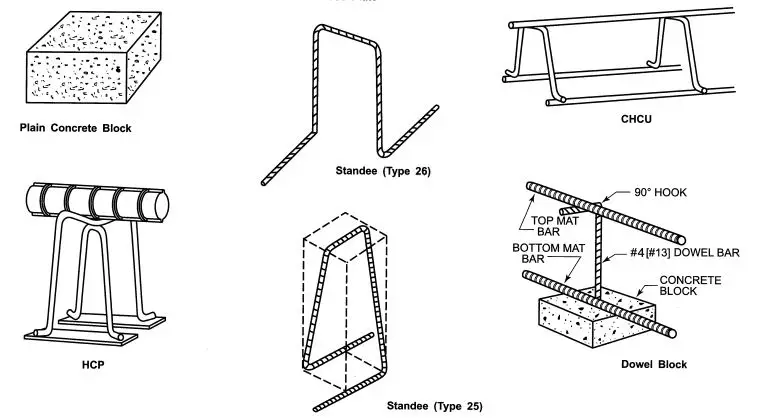
Examples of Bar Supports for Foundation Mats and Slabs on Ground
- Plain Concrete Block: Suitable for heights up to 6 inches (152 mm).
- All-Plastic Chair with Base Plate: Suitable for heights up to 6 inches (152 mm).
- HCP (High Chair with Sand Plate): An individual chair with a sand plate for soil bearing, suitable for heights up to 15 inches (381 mm).
- CHCU (Continuous High Chair Upper): Continuous runner wires provide support for the lower mat of reinforcing bars, suitable for heights up to 15 inches (381 mm).
- Standee: A custom-fabricated reinforcing bar with bent legs resting on the lower mat of bars.
- Dowel Block: A precast block with a hole for a #4 (#13) dowel bar, suitable for supporting both the top and bottom mats of bars, with heights up to 2 feet (610 mm).
Recommended Practices for Bar Support Usage Based on Slab Thickness
- Slabs up to 2 feet (600 mm) thick: HCP, Plain Concrete Block, All-Plastic Chair with Base Plate, CHCU, Standees using #4 (#13) bars, or dowel blocks (applicable to Western States only).
- Slabs more than 2 feet (600 mm) and up to 4 feet (1200 mm) thick: Standees using #5 (#16) bars.
- Slabs more than 4 feet (1200 mm) thick: Bar supports are generally not provided unless arranged for specifically.
Conclusion
Rebar standees are indispensable components in reinforcing concrete structures, offering stability and reinforcement to prevent cracking and enhance structural integrity.
By understanding the types of rebar standees available and considering key design factors, engineers and construction professionals can ensure the successful implementation of these essential support systems.