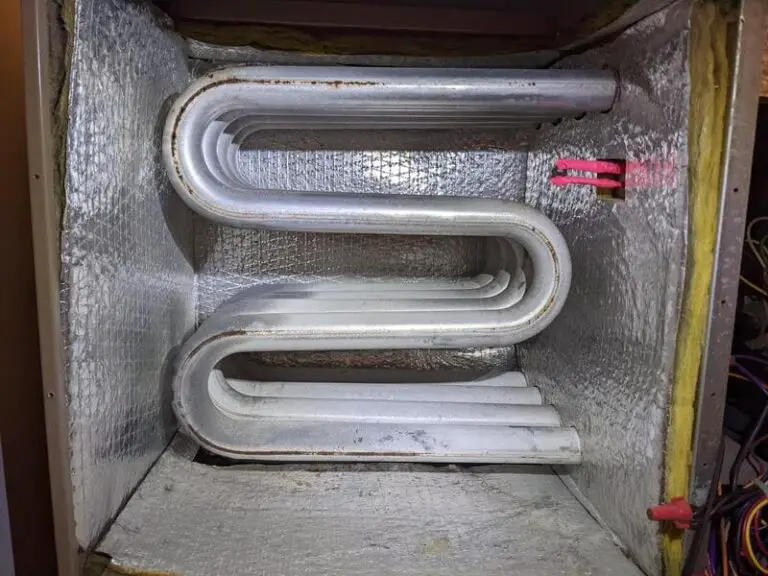
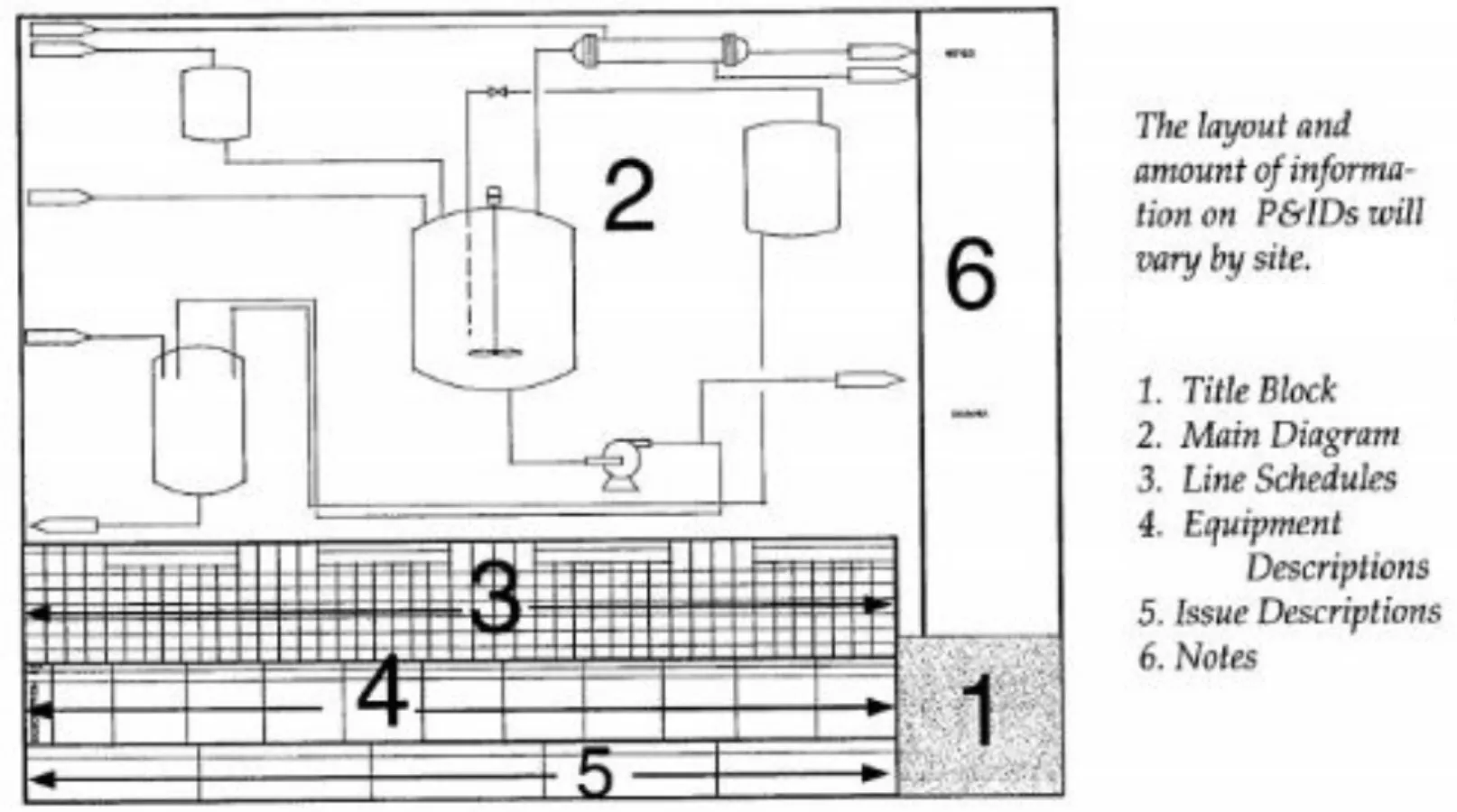
As the temperature drops and winter sets in, the trusty furnace becomes a vital component of every household. However, nestled within this heating system lies a crucial yet often overlooked component – the heat exchanger. While it may not be as visible or talked about as other parts of the furnace, the heat exchanger plays a pivotal role in ensuring efficient and safe heating for your home.
In this article, we will get insight into the inner workings of furnace heat exchangers, exploring their significance in ensuring comfort and safety while unraveling their fascinating role in keeping us warm during cold winter nights.
Furnace heat exchanger importance
A furnace heat exchanger is essentially a device that transfers heat from one medium to another without them coming into direct contact.
“In simple terms, it’s responsible for extracting heat from burned fuel (such as natural gas or oil) and transferring it to the air circulated throughout your home. Without these ingenious devices, our furnaces would simply blow cold air and fail in their primary purpose – providing warmth and comfort.“
But why should homeowners care about this seemingly technical aspect of their heating systems?
The truth is, understanding how furnace heat exchangers work can shed light on energy efficiency levels, maintenance requirements, potential risks associated with malfunctioning units, and even cost considerations when upgrading or replacing furnaces.
How Furnace Heat Exchangers Work?
Furnace heat exchangers play a crucial role in the efficient and safe operation of residential furnaces. These devices are responsible for transferring heat from combustion gases to the air that flows through your home’s ventilation system.
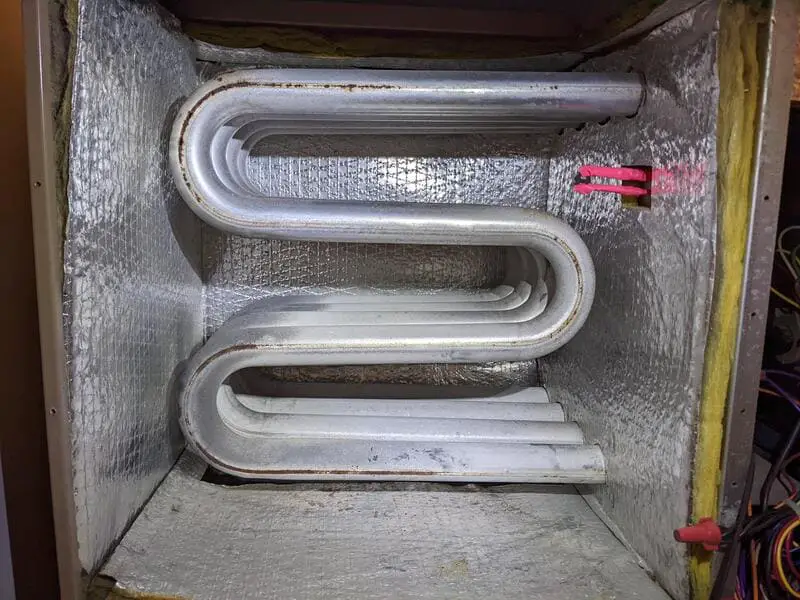

There are different types of furnace heat exchangers, but they all operate on the same basic principles. One common design is the tubular heat exchanger, which consists of a series of metal tubes that carry combustion gases. The walls of these tubes absorb the heat from the hot gases as they pass through.
- The process begins with the burner inside your furnace igniting a mixture of fuel and air to create combustion gases, typically including carbon dioxide, water vapor, nitrogen oxide, and other byproducts.
- As these hot gases flow through the flue passage or plenum chamber surrounding the furnace’s primary assembly area, their contact with the metal walls causes them to transfer thermal energy.
- Next, indoor air from your living space is pulled into another section of tubing adjacent to but separated from where combustion occurs. This secondary airflow passes over or around the heated pipes within what’s called an ‘air-to-air’ exchange system.
- The result: cold indoor air warms up as it absorbs heat radiating off those glowing surfaces before being distributed back into rooms throughout your home via ductwork connected to vents or registers placed strategically in different areas.
In summary, when you turn on your furnace and set it to warm up your home during colder months or cool it during warmer ones (in cases where there’s also an integrated AC coil), one critical element at play behind this temperature transformation process is none other than its trusty furnace heat exchanger working diligently behind-the-scenes!–and ultimately determining how efficiently that comfort need will be met without risking health hazards associated with exposure to harmful emissions such as carbon monoxide produced during incomplete combustion events.
Applications of Furnace Heat Exchangers
Residential heating is the primary application of furnace heat exchangers, making them an essential component in standard home heating systems.
As homeowners look for efficient and cost-effective ways to keep their homes warm during colder months, furnaces with heat exchangers have become a popular choice.
- One of the main benefits of furnace heat exchangers is their contribution to energy efficiency. These devices play a crucial role in recovering waste heat from combustion gases and transferring it into the indoor air that circulates throughout the house.
- By harnessing this wasted energy, furnaces can achieve much higher levels of efficiency compared to older models without heat exchangers. This results in significant savings on fuel consumption and lowers utility bills for homeowners.
- In addition to saving money, using a furnace with a heat exchanger also has positive environmental impacts. By maximizing fuel efficiency through waste heat recovery, less carbon dioxide emissions are released into the atmosphere when heating homes. This means that not only are homeowners able to reduce their energy costs but they can also decrease their carbon footprint at the same time.
Furnace manufacturers recognize these advantages and have embraced the use of heat exchangers as part of their commitment towards more sustainable and eco-friendly solutions for residential heating needs.
Cost Considerations
The cost of installing or replacing a furnace with an effective heat exchanger can vary depending on several factors. One important consideration is the size and capacity of the furnace needed to adequately heat the space. Larger homes or buildings may require more powerful, and therefore more expensive, furnaces.
Another factor that influences cost is the efficiency rating of the furnace. Energy-efficient models are typically pricier upfront but can provide significant long-term savings through reduced energy consumption. It’s worth considering this upfront investment as it can result in lower utility bills over time.
Additionally, installation costs should be taken into account when budgeting for a new heat exchanger-equipped furnace. Hiring professional HVAC technicians ensures proper installation, which may increase the overall expense but guarantees optimal functionality and efficiency.
While the initial cost might seem high, choosing a high-quality furnace with an efficient heat exchanger can deliver substantial benefits in terms of energy savings and comfort for years to come. Taking into account both short-term expenses and long-term potential savings will help homeowners make informed decisions about their heating systems while keeping their budgets in check.
Limitations and Potential Concerns
While furnace heat exchangers offer numerous benefits, it’s important to be aware of their limitations and potential concerns. One major issue that homeowners should be mindful of is the risk of carbon monoxide leaks.
The combustion process in a furnace produces this harmful gas, which can leak through cracks or gaps in a damaged heat exchanger. To avoid this danger, it’s crucial to install carbon monoxide detectors in your home and schedule regular inspections by trained professionals.
Maintenance requirements are another factor to consider when it comes to furnace heat exchangers. Over time, a buildup of dirt, dust, and debris can occur inside the heat exchanger tubes if not regularly maintained. This accumulation can impede airflow and decrease efficiency. Therefore, it’s important to have your furnace inspected annually and cleaned as needed by a qualified HVAC technician.
It’s worth noting that replacing a failed heat exchanger can be an expensive endeavor. Depending on the age of your furnace and the availability of replacement parts, costs could range from several hundred dollars to over a thousand dollars for both materials and labor.
Considering this potential expense, it becomes even more critical to invest in routine maintenance for your furnace heat exchanger – preventing premature failure while ensuring safe operation throughout its lifespan.
Key Takeaways:
- Furnace heat exchangers play a crucial role in the efficient and safe operation of residential heating systems. They work by transferring heat from the combustion process to the surrounding air, allowing for warm and conditioned air to be distributed throughout the home.
- One of the main benefits of furnace heat exchangers is their ability to improve energy efficiency. By maximizing the transfer of heat from combustion gases, these devices help minimize fuel consumption and reduce utility bills. Additionally, modern furnace heat exchangers are designed with safety features that prevent carbon monoxide leaks, preserving indoor air quality.
- While furnace heat exchangers offer numerous advantages, it’s important to consider some limitations as well. Over time, these components may develop cracks or rust which can lead to inefficiency and potential carbon monoxide risks if not addressed promptly. Regular maintenance and inspections by HVAC professionals are crucial to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how furnace heat exchangers work can empower homeowners to make informed decisions about their heating systems. By investing in high-quality units and maintaining them properly, individuals can enjoy improved energy efficiency, reduced environmental impact, lower costs on utility bills while ensuring a comfortable living environment all year round.