When buying steel products such as plates, pipes, or bars, the manufacturer is required to provide a material certificate, commonly referred to as a Mill Test Certificate (MTC), to the buyer.
This MTC details all specifications of the steel products, including weight, dimensions, chemical composition, mechanical properties, heat treatment status, test results, and heat traceability. It serves as a declaration that the quality of the steel products has been reliably verified. The standards for inspection and certification were previously outlined in the German standard DIN 50049.
In 1991, the definitions for material testing and certificate types established in DIN 50049 were adopted as the European standard EN 10204. This led to the classification of certificate types: 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 3.1A, 3.1B, 3.1C, and 3.2, all of which follow the guidelines of DIN 50049.
What is a Material Certificate?
A Material Certificate, or MTC, is a document that verifies the chemical, mechanical, and physical properties of a material. It is also known as a Mill Certificate or Test Certificate.
The MTC is crucial for manufacturers and suppliers, as it confirms the quality of the material. The certificate includes details on the material’s chemistry and heat treatment, as well as physical properties like density, strength, and hardness.
BS EN 10204 or DIN EN 10204 is a European standard that specifies the types of inspection documentation required for the supply of metallic products. It can also apply to non-metallic products if agreed upon at the time of ordering. The certification types defined in EN 10204 include:
- Type 2.1
- Type 2.2
- Type 2.3 (included in Type 3.1 certificate)
- Type 3.1
- Type 3.2
Changes in EN 10204 Material Inspection Document
In October 2004, EN 10204 was revised and issued as BS EN 10204:2004. This update streamlined the inspection documents into four categories specifically for metallic products, now recognized as types 2.1, 2.2, 3.1, and 3.2. Notably, the following changes were made:
| EN 10204:1991 | EN 10204:2004 |
|---|---|
| Certificate type 2.3 | Deleted |
| Certificate type 3.1B | Changed to Certificate type 3.1 |
| Certificate types 3.1A, 3.1B, 3.2 | Consolidated into Certificate type 3.2 |
What is the Difference Between 2.2 and 3.1 Material Certificates?
A Type 2.2 Test Certificate serves as a Test Report that confirms compliance based on historical test data without testing the actual material. The manufacturer certifies that the material supplied under this certificate meets the specified requirements, and it is validated solely by the manufacturer.
In contrast, a Type 3.1 Certificate provides actual test results for the material supplied. The product manufacturer certifies this test certificate, ensuring that the product meets material standards. Type 3.1 certification is validated by an independent inspector who is authorized and separate from the manufacturing department.
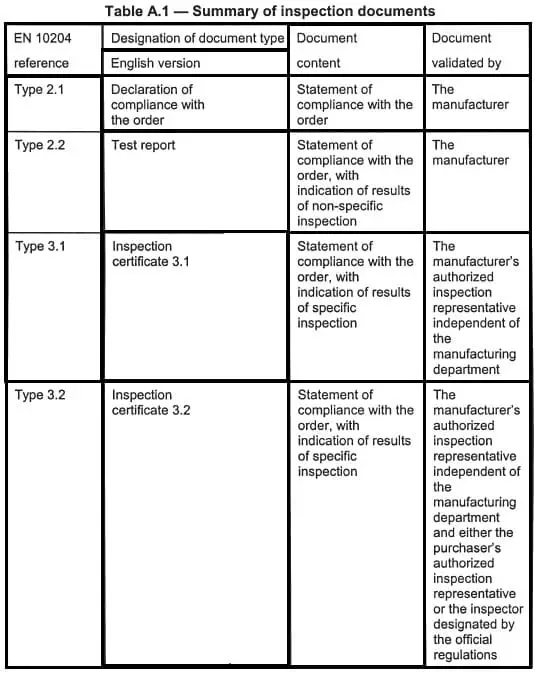
Summary of Inspection Document Types
Here’s a summary of the inspection documents as per EN 10204 for types 2.1, 2.2, 3.1, and 3.2:
| Certificate Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Type 2.1 | Declaration of compliance without testing |
| Type 2.2 | Test Report based on historical data, not physically tested |
| Type 3.1 | Inspection Certificate with actual test results |
| Type 3.2 | Inspection Certificate with additional verification |
Difference Between 3.1 and 3.2 Material Certification
Both Type 3.1 and Type 3.2 certificates are inspection documents that confirm compliance with material standards based on actual test results.
- Type 3.1 Inspection Certificate: This certificate includes the actual test values for a batch of steel products supplied. It is issued by the manufacturer and certifies that the product meets the specified material standards. The validation comes from a manufacturer-authorized inspector who is independent of the production department.
- Type 3.2 Inspection Certificate: Similar to Type 3.1, this certificate also includes actual test results but is additionally signed and verified by an independent third-party inspector. This inspector may be an external authorized inspector or a representative from a regulatory body. The Type 3.2 certificate ensures that the product has been tested under specific quality requirements and meets the minimum standards.
Difference Between 2.1 and 2.2 Certification
- Type 2.1 Material Certificate: This is a Certificate of Compliance (CoC) that serves as a declaration from the manufacturer that the product meets the required specifications without any physical testing. It does not include test results.
- Type 2.2 Material Certificate: This is a test report where the manufacturer certifies that the supplied product complies with the purchase order requirements. Unlike Type 2.1, it provides results from non-specific tests but does not reflect actual material properties.
Difference Between 2.1 and 3.1 Certification
- Type 3.1 Material Certificate: This document verifies the chemical and physical properties of a material through testing conducted by an accredited laboratory. It includes detailed information about the material’s composition, mechanical properties, and thermal properties. A Type 3.1 certificate is crucial for ensuring compliance with safety and performance standards.
- Type 2.1 Material Certificate: As mentioned earlier, this is a compliance certificate that indicates the manufacturer asserts the product meets specified requirements without any testing. It lacks test results.
What is a 3.1 Material Certificate?
A 3.1 Material Certificate verifies the chemical and physical properties of a material, issued by an accredited testing laboratory. It provides detailed information about the material’s composition, mechanical properties, and thermal properties. This certificate is essential for confirming that materials meet safety and performance requirements, ensuring that the supplied material has been tested to meet the minimum standards.
There are two classifications of Type 3.1 certification based on the level of issuing authority:
- Type 3.1
- Type 3.2
What is a 3.2 Material Certificate?
A Type 3.2 Material Certificate is a comprehensive inspection document that verifies both the chemical and physical properties of a specific material. This certificate is validated by two inspectors: one appointed by the manufacturer and one appointed by the purchaser or designated by official regulations. Both inspectors confirm that the supplied products meet the requirements specified in the purchase order, including detailed test results.
The 3.2 designation indicates that the certificate complies with the European standard EN 10204. Manufacturers and suppliers commonly use this certificate to ensure that their materials adhere to industry standards.
What is a 2.1 Material Certificate?
A Type 2.1 Material Certificate is known as a Certificate of Compliance (CoC). This document, certified by the manufacturer, asserts that the material meets specified requirements without any actual testing. It does not include test results, and the manufacturer assumes responsibility for ensuring that the material possesses the minimum required mechanical and chemical properties.
What is a 2.2 Material Certificate?
A Type 2.2 Material Certificate serves as a test report. In this case, the manufacturer certifies that the supplied products comply with the purchaser’s requirements based on other inspections and tests. The certificate includes results from non-specific tests rather than actual material properties, providing a general assurance of compliance without detailed testing on the supplied material.
EN 10204 Type 3.1 Certificate Example
An EN 10204 Type 3.1 Certificate is a document that certifies the quality of a product. Typically issued by the manufacturer, this certificate indicates that the product has been manufactured according to specific standards. It provides critical information about the product, including its dimensions, weight, and verified test results, ensuring that it meets the necessary quality requirements.