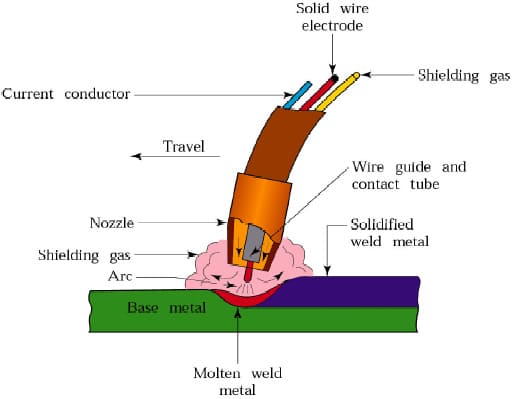
Welding is a versatile and essential process in various industries, enabling the fabrication and joining of metal components. One popular welding method is MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, which traditionally utilizes a shielding gas to protect the weld pool from atmospheric contamination.
However, there is an alternative technique known as gasless MIG welding, which eliminates the need for an external shielding gas. In this blog post, we will learn about the gasless MIG welding, exploring its benefits, applications, and key considerations.
The self-shielded flux-cored arc welding (FCAW) process has become a preferred choice among contractors due to its numerous advantages, including increased productivity and potential cost savings in labor. Recent advancements in self-shielded FCAW wires have made them easier to use and capable of delivering superior weld quality, further enhancing their appeal to contractors.
By utilizing self-shielded FCAW wires, contractors can benefit from higher productivity, ultimately saving time and money on labor-intensive projects. These wires have undergone significant improvements, making them more user-friendly and capable of producing higher-quality welds than ever before. As a result, they have gained popularity among contractors who seek efficiency and superior results.
Understanding Gasless MIG Welding
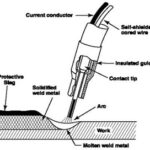
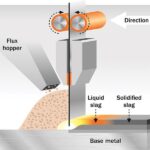
Gasless MIG welding, also referred to as flux-cored arc welding (FCAW), employs a tubular wire electrode filled with flux. This flux acts as a shielding agent, protecting the molten weld pool from oxygen and other atmospheric contaminants. The flux also generates a slag that covers the weld bead, providing additional protection during the cooling process.

Gasless MIG Welding Wires
When it comes to gasless MIG welding wires, two common types are widely used in construction applications: those meeting the American Welding Society (AWS)
- E71T-11 and
- E71T-8 classifications.
These wires, also known as T-11 and T-8, are highly versatile options suitable for structural applications and can be used in all positions for general welding purposes.
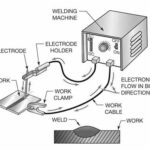
Selecting the appropriate equipment is crucial when working with either T-11 or T-8 wires. It is recommended to use a constant voltage (CV) power source instead of a constant current (CC) power source.

CC power sources tend to fluctuate too much when paired with these wires, leading to inconsistent weld quality and defects like porosity. On the other hand, a CV power source delivers a consistent voltage, ensuring smooth arc performance. It is particularly effective in compensating for “dirty power” situations on job sites, where high and low spikes in power occur due to multiple loads sharing the same line (e.g., compressors and power sources).
Both T-8 and T-11 wires should be operated using DCEN (direct current electrode negative) or straight polarity, which is the opposite of most wire filler metals. It is essential to note that using the wrong polarity can result in poor welding performance and increased spatter levels.
In addition to considering equipment requirements, many welders opt to use suitcase wire feeders, which are robust, portable feeders that enclose and protect the wire. These feeders enhance portability on construction sites, allowing for greater flexibility during welding tasks.
Gas vs Gasless mig welding?
In most welding types, shielding gases from external cylinders have long been used to protect weld joints from oxygen and prevent issues such as porosity and excessive spatter.
However, gasless welders take a different approach by utilizing “self-shielding wire.”
Essentially, self-shielding wire is a metal tube with a core of flux. When the wire is heated during welding, the flux burns and generates a shielding gas. This gas acts as a protective barrier, preventing oxidation and contamination of the welding joint without the need for an external gas cylinder.
To achieve better results with a gasless MIG welder, here are five essential tips:
- Choose the Correct Welding Polarity: It’s crucial to understand that not all welders are compatible with self-shielding wire due to the polarity requirements. Welding torches must have the appropriate polarity for the wire being used.
- There are three main types of welding polarity:
- DC Straight Polarity: The electrical current flows from the electrode to the welding surface, generating significant heat on the welding surface. DC
- Reverse Polarity: The electrical current flows from the welding surface to the electrode, concentrating the heat on the electrode itself.
- Alternating Polarity: The current direction alternates and is primarily used for large industrial applications.
- A gasless MIG welder necessitates a welding gun with DC reverse polarity. Using straight polarity with self-shielding wire will yield unsatisfactory results, including excessive splatter around the joint. This not only affects the appearance but can also lead to structural issues if the wire splatters onto unintended areas of the welding surface.
- Check Welder Polarity Options: Most modern MIG welding machines offer the flexibility to be set to either straight or reverse polarity. However, if your welder only offers straight polarity, it is not suitable for gasless welding. It’s important to ensure that your welder is compatible with the required reverse polarity for gasless welding.
Benefits of Gasless MIG Welding
- Portability and Convenience: Gasless MIG welding offers increased portability compared to traditional MIG welding setups. Without the need for a gas cylinder, welders can maneuver more freely and access hard-to-reach areas. This makes gasless MIG welding an excellent choice for on-site repairs and outdoor projects.
- Cost-Effective Solution: Gasless MIG welding eliminates the expense of purchasing and refilling shielding gas cylinders. The flux-core wire used in this process is typically more economical than solid MIG wire, making it a cost-effective option for welding applications.
- All-Position Welding: Gasless MIG welding excels in all-position welding, including vertical and overhead positions. The flux in the wire provides better penetration and weld bead control, allowing for high-quality welds in various orientations.
- Enhanced Penetration and Strength: The flux-cored wire used in gasless MIG welding typically contains deoxidizing agents and alloying elements. This composition enhances weld penetration and provides improved strength and impact resistance, making it suitable for challenging applications.
Applications of Gasless MIG Welding
- Automotive Repairs: Gasless MIG welding finds extensive use in automotive repairs, such as fixing body panels or exhaust systems. Its portability and ability to weld thicker materials make it ideal for repairing vehicles on-site or in auto body shops.
- Construction and Maintenance: Gasless MIG welding is valued in construction and maintenance projects, including welding structural steel, heavy equipment repairs, and infrastructure maintenance. Its versatility and accessibility enable welders to tackle a wide range of applications.
- Farm and Ranch Work: Gasless MIG welding is popular among farmers and ranchers for repairs and fabrication tasks. From fixing fences and gates to constructing equipment, gasless MIG welding offers the convenience and reliability required in agricultural settings.
Considerations for Gasless MIG Welding
- Proper Wire Selection: Choosing the right flux-core wire for your specific application is crucial. Factors such as material type, thickness, and desired weld characteristics should be considered when selecting the appropriate wire.
- Adequate Ventilation: While gasless MIG welding eliminates the need for an external shielding gas, it produces more smoke and fumes due to the flux-core wire. Adequate ventilation or the use of local exhaust ventilation systems is necessary to maintain a safe and healthy working environment.
- Welding Technique: Gasless MIG welding requires specific techniques for optimal results. It is essential to maintain a consistent travel speed, electrode angle, and distance between the nozzle and workpiece. Practice and familiarity with the process will help achieve high-quality welds.
Main Advantages of Gasless MIG Welding
- Ideal for outdoor welding due to no reliance on shielding gas affected by wind.
- Suitable for welding thick materials, such as structural steel and heavy equipment.
- Often used for field repairs due to easy transportation and strong welds.
- Popular choice for DIY welding projects due to ease of use and cost-effectiveness.
- Capable of welding dirty or rusty metals by removing contaminants during the process.
- Not recommended for applications requiring high-quality welds on aluminum or stainless steel.